
Tailings Dam Monitoring with InSAR & AI
Tailings Dam Monitoring: How Advanced Satellite Intelligence Is Transforming Tailings Dam Safety Tailings dams are among the most critical—and high-risk—structures
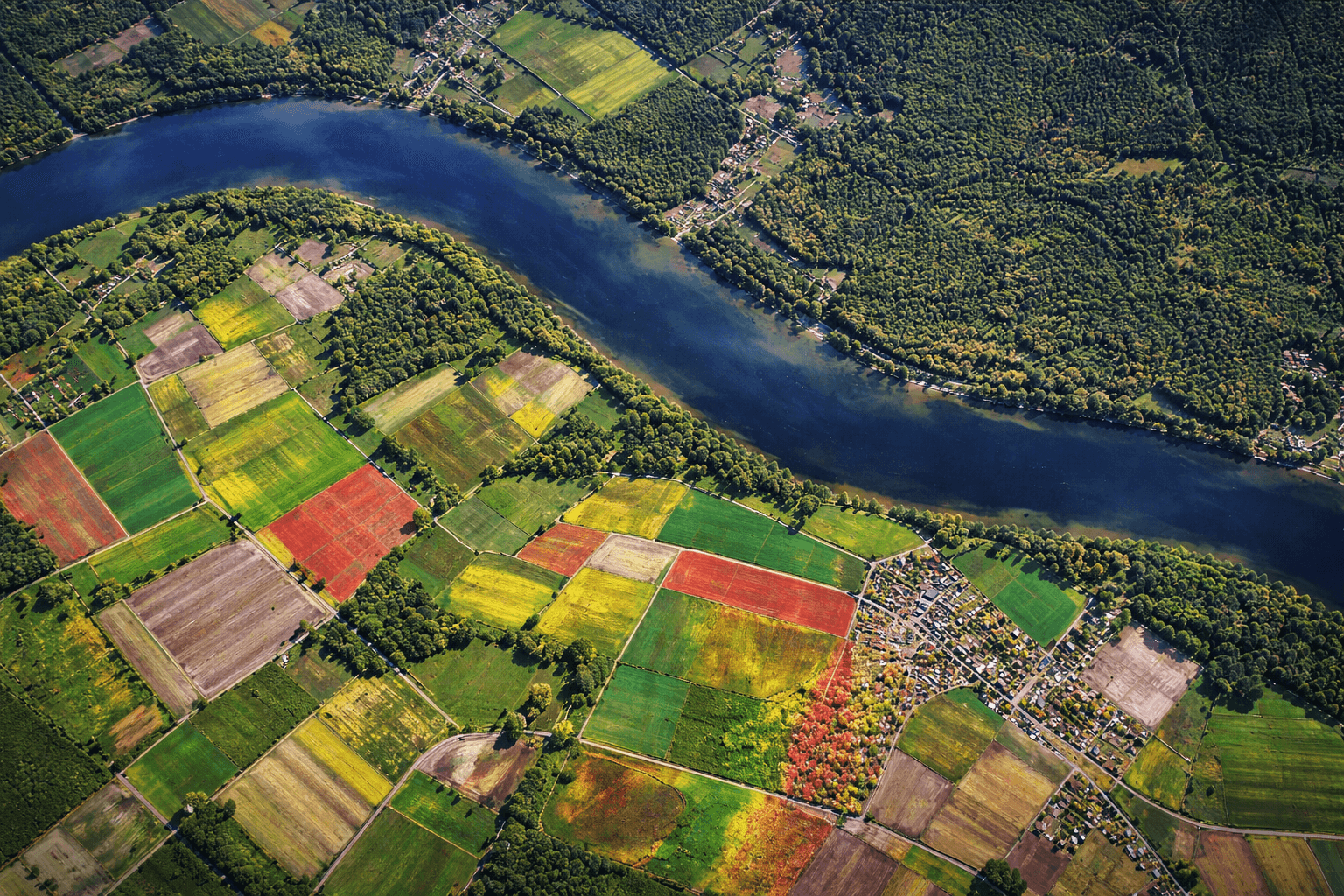
Stereo Satellite Imagery opens up an exciting new way to explore the Earth’s surface, offering unmatched 3D insights and precise elevation details. This advanced technique captures overlapping images from two slightly different angles, creating a stereoscopic view similar to how human eyes perceive depth. By combining these images, detailed 3D models of the Earth’s surface are produced, providing valuable data for mapping, analysis, and visualization. The method relies on the parallax principle, which explains how objects appear to shift in perspective based on viewing angles. This parallax effect is leveraged in satellite photography to deliver highly accurate three-dimensional representations.
Stereo imagery is created by either merging images from multiple satellite passes or using sensors designed with multiple viewing angles. Some satellites even have dual sensors that capture images from slightly different perspectives simultaneously, ensuring high-quality stereo pairs for precise 3D modeling. The integration of Stereo Satellite Imagery into GIS workflows has revolutionized spatial analysis, enabling better visualization and understanding of complex terrains. This article delves into the technical aspects of stereo imagery, its practical applications, and its growing importance in geospatial studies.
Stereoscopy is the technique of presenting two slightly shifted images to the left and right eyes separately, creating a realistic sense of depth. In satellite imagery, this is achieved by capturing two separate images of the same area on Earth. These stereo pairs allow us to measure topographical features accurately and build detailed three-dimensional (3D) models of the Earth’s surface.
Satellites equipped with high-resolution optical sensors are used to capture these stereo images. Often, satellites with stereo imaging capabilities take images of the same location from different angles or after a brief delay. This ensures the generation of precise stereo pairs needed for creating high-quality 3D models. With higher resolutions, these models offer exceptional accuracy and detail. To further enhance precision, accurate georeferencing aligns the images correctly, making stereo satellite imagery an invaluable tool for understanding Earth’s landscapes.
Stereo satellite imagery uses two key components to create detailed and accurate 3D visuals:
Satellite Sensors: Satellites designed for stereo imagery are fitted with advanced sensors that capture crystal-clear pictures. These sensors can take high-resolution images, sometimes as sharp as 30 cm, providing stunning detail and accuracy.
Overlapping Image Pairs: The secret behind stereo imagery is the overlapping images taken from different angles. This overlap creates a parallax effect, making it possible to calculate depth and elevation when the images are processed together.
This combination of high-tech sensors and overlapping visuals makes stereo satellite imagery a powerful tool for precise mapping and analysis.
Stereo imagery gives urban planners and architects the tools to create detailed 3D models of cities and towns. By visualizing construction scenarios and assessing how new infrastructure integrates with existing landscapes, it enables smarter decisions that optimize space while minimizing environmental impact. It also helps develop more accurate flood models for disaster preparedness, allowing better risk assessment and enhanced simulations of potential flood scenarios.
For conservation efforts, stereo imagery plays a crucial role in analyzing natural habitats and ecosystems. This technology helps monitor deforestation, track vegetation changes, and assess land use patterns, all supporting sustainable environmental management and conservation initiatives.
In the face of natural disasters like earthquakes, floods, or wildfires, stereo satellite imagery becomes a vital resource. The 3D models it generates provide a clear and rapid overview of affected areas, aiding emergency responders in planning and resource allocation to minimize damage and save lives.
Farmers benefit from stereo imagery’s detailed analysis of crop health and terrain mapping. It helps identify crop stress, monitor growth patterns, and detect irrigation issues, allowing farmers to refine their practices, reduce waste, and maximize yields with minimal environmental impact.
Archaeologists leverage stereo imagery to uncover ancient sites and hidden structures buried beneath the surface. By enabling 3D visualization of landscapes, it aids in reconstructing historical locations and gaining deeper insights into ancient civilizations.
Stereo imagery is essential for creating precise topographic maps, which provide detailed elevation data. These maps are indispensable for environmental studies, infrastructure projects, and urban planning, offering clear and comprehensive terrain insights.
Stereo satellite data is key to developing Digital Elevation Models (DEMs), which display continuous elevation values across the Earth’s surface. DEMs support GIS applications, including line-of-sight analysis, slope evaluation, and hydrological modeling, enhancing decision-making in various fields.
With stereo imagery, change detection becomes seamless by capturing the same area over time. It identifies shifts in infrastructure, natural features, or land cover, enabling analysts to monitor urban growth, deforestation, and environmental changes with precision.
Stereo imagery simplifies the creation of 3D city models, enabling urban planners to analyze spatial arrangements and assess the impact of new developments. This is particularly valuable for zoning, infrastructure upgrades, and evaluating the integration of new projects into existing urban frameworks.
Stereo imagery is a powerful tool that can transform how industries analyze, plan, and make decisions. By understanding its applications and utilizing specialized tools, businesses and organizations can unlock its full potential. Here’s how you can effectively leverage stereo satellite imagery:
Selecting the appropriate stereo satellite imagery platform is crucial. Opt for providers that offer high-resolution images tailored to your needs, such as urban planning, agriculture, or environmental monitoring. Platforms like XRTech provide access to a wide range of stereo imagery data, ensuring versatility and precision.
Processing stereo imagery requires specialized software capable of handling 3D data extraction, terrain analysis, and elevation modeling. Tools for orthorectification, mosaicking, and image adjustment are vital for converting raw imagery into actionable insights.
Create Digital Elevation Models using stereo imagery to map terrain and elevation with precision. DEMs are instrumental in applications like flood modeling, slope analysis, and infrastructure development.
Leverage stereo imagery to track changes over time. Use it to identify shifts in land cover, monitor urban expansion, or assess environmental impacts. Accurate change detection allows for timely interventions and informed planning.
Transform stereo imagery into detailed 3D models to visualize urban environments, natural landscapes, or archaeological sites. These models help stakeholders make better decisions by offering a realistic perspective of their areas of interest.
Ensure your team is equipped to analyze and interpret stereo imagery effectively. Training on data visualization, analysis tools, and geospatial interpretation can maximize the value derived from stereo imagery.
By combining the right tools, expertise, and applications, stereo satellite imagery can enhance decision-making, optimize operations, and drive innovation across various industries.
Choosing the right satellite for stereo imagery depends on your specific goals and the nature of the project. Factors such as resolution, coverage, and imaging capabilities play a crucial role in ensuring accurate and actionable data. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you make an informed choice:
Start by clearly identifying the purpose of your project. Are you focusing on:
Resolution is key to stereo imagery. Depending on your needs:
Different satellites offer unique imaging technologies:
The frequency of image capture is critical:
Choose a satellite based on your area of interest:
High-resolution and specialized imagery can be costly. Balance your needs with available resources and explore providers offering tailored solutions, like XRTech, for cost-effective options.
By aligning your project requirements with satellite capabilities, you can ensure the stereo imagery you choose delivers the precision and insights necessary for success.
Stereo imagery has already proven to be an essential tool in many industries, offering deep insights through 3D visualizations and data-driven solutions. As technology continues to evolve, the future of stereo imagery looks even more promising, with advancements in satellite technology, artificial intelligence (AI), and data analytics paving the way for smarter and more efficient applications. Here’s a look at what we can expect in the coming years:
Future satellites will capture higher resolution stereo imagery, enabling even more detailed 3D models and accurate data. With advancements in sensor technology and imaging systems, stereo imagery will be able to provide finer details, which will improve applications like urban planning, environmental monitoring, and infrastructure development. This will allow for precision down to a few centimeters or even millimeters, offering an unmatched level of detail for critical decision-making.
One major development on the horizon is the ability to capture stereo images more frequently. With new satellites being launched and AI algorithms improving image processing, the revisit times for certain areas will be reduced. This means real-time or near-real-time data will be available for industries like disaster management, agriculture, and urban development, where timely decisions are critical.
Artificial Intelligence and machine learning will play a pivotal role in the future of stereo imagery. By combining AI with stereo satellite imagery, industries can automatically detect changes in landscapes, predict trends, and even identify patterns that were previously invisible. For example, AI could help automatically track deforestation, monitor crop health, or assess infrastructure stress, allowing faster and more accurate responses.
As satellite technology becomes more affordable and accessible, the cost of obtaining high-quality stereo imagery will decrease. This will democratize the use of this technology, allowing smaller businesses, local governments, and even individuals to leverage stereo imagery for various purposes. Open-source platforms and easier access to satellite data will encourage innovation in industries like environmental conservation, urban planning, and agriculture.
In the future, stereo imagery will evolve to provide real-time 3D mapping. This will be particularly beneficial in areas like emergency response, where immediate and accurate spatial data is crucial. Real-time 3D models of disaster zones will help responders assess damage, allocate resources, and plan interventions more effectively. In urban settings, this can lead to more dynamic city planning and smarter infrastructure development.
The future of stereo imagery will likely involve multi-layered and multispectral data, meaning stereo images will combine different wavelengths (like infrared, thermal, and radar) to provide deeper insights. This will allow industries to monitor not just the surface, but also the health of ecosystems, the movement of wildlife, and even the underground structures, like utilities or archaeological sites.
Stereo imagery is a powerful tool that offers unparalleled benefits across a variety of industries, from urban planning and environmental monitoring to disaster management and agriculture. By providing 3D visualizations and accurate topographic data, it allows professionals to make better-informed decisions, optimize resources, and track changes over time.
The ability to create detailed 3D models of cities, assess crop health, monitor environmental changes, and respond to disasters efficiently makes stereo satellite imagery an indispensable resource in today’s fast-evolving world. With advancements in technology, including AI-driven analytics and high-resolution satellites, the potential applications for stereo imagery are vast and continuously growing.
Ultimately, whether you’re looking to monitor infrastructure, enhance land conservation efforts, or manage natural disasters, stereo imagery empowers you with the data and insights needed to make impactful, data-driven decisions. As the technology evolves, its ability to provide timely, accurate, and actionable information will only continue to improve, unlocking new possibilities for a wide range of industries.

Tailings Dam Monitoring: How Advanced Satellite Intelligence Is Transforming Tailings Dam Safety Tailings dams are among the most critical—and high-risk—structures
From Visible Light to Spectral Intelligence in Modern Satellite Remote Sensing Satellite imaging has moved beyond photography. For decades, Earth