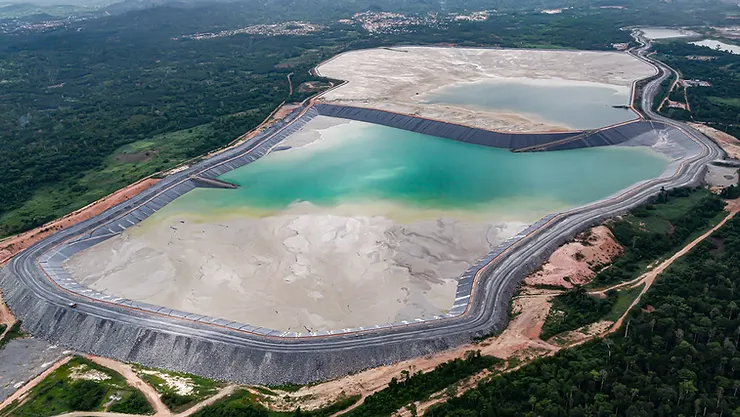

Tailings Dam Monitoring with InSAR & AI
Tailings Dam Monitoring: How Advanced Satellite Intelligence Is Transforming Tailings Dam Safety Tailings dams are among the most critical—and high-risk—structures
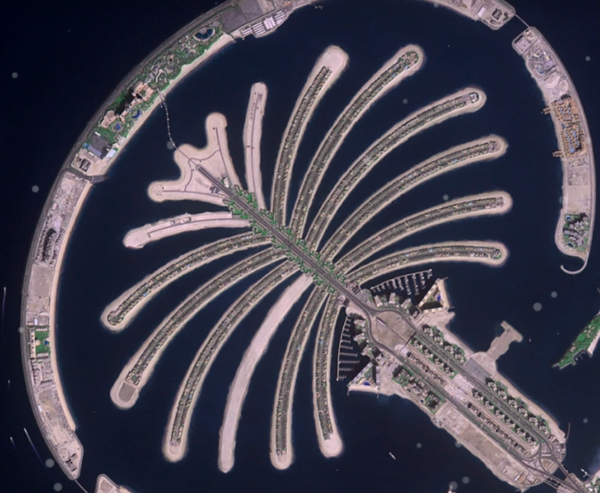
Satellite imagery has revolutionized the way we see and understand our world. Have you ever wondered how satellites capture detailed pictures of the Earth’s surface from space? These images, captured by satellites orbiting our planet, help us monitor changes on Earth, track weather patterns, and even plan new cities. Whether you want to explore forests, monitor crops, or track urban growth, satellite imagery makes it all possible. It provides us with high-resolution data that’s crucial for countless industries, making it one of the most powerful tools today. In this guide, we’ll take a deep dive into what satellite imagery is, the different types available, and how you can access these incredible images. Let’s explore how these images can benefit you and your work in ways you never thought possible!
Read: 19 Free Sources of High-Resolution Satellite Imagery
Read: Can I See Live Satellite Images of My House?
Read: High-Resolution Satellite Images by XRTech Group
Read: Best Drone with Thermal Camera

Satellite imagery is the process of capturing high-resolution visual data from the Earth’s surface using satellites that orbit our planet. These satellites are equipped with advanced cameras and sensors that gather images from space. These images can show various types of data, from simple black-and-white pictures to colorful, multi-spectral images. Satellite imagery helps us see the world in new ways by collecting light, infrared, and even microwave data that can be used to create detailed pictures of the Earth.
Satellites use different kinds of sensors to gather information. Some sensors, known as passive sensors, collect sunlight that is reflected off the Earth, while others, called active sensors, send out their own signals and measure how they bounce back. Unlike passive sensors, active sensors can be used at night or during cloudy weather because they don’t rely on sunlight. This makes satellite imagery useful no matter the time of day or weather conditions.
Today, satellite imagery is an essential tool in many industries. It helps us track changes in the environment, such as deforestation or urban growth, and plays a key role in responding to natural disasters like floods or wildfires. By analyzing the detailed data captured from space, experts can make better decisions about city planning, transportation routes, and disaster management. Whether it’s monitoring climate change or planning new infrastructure, satellite imagery provides a unique, bird’s-eye view of the world that allows us to make smarter, more informed choices.
For industries and leaders involved in technology, keeping up with the latest trends in satellite imagery is important. This technology helps solve large-scale challenges and provides a fresh perspective on the world, which is why satellite imagery continues to innovate solutions for a rapidly changing world.
Satellite imagery is an amazing tool that helps us see the world from space! It works by using special sensors on satellites that orbit the Earth, capturing detailed pictures and data about our planet. But how exactly does it work? Let’s break it down.
Satellites can be sent into different orbits around the Earth depending on their job. Two common types of orbits are polar orbits and geostationary orbits. Polar orbits pass over the Earth’s poles and allow satellites to see almost every part of the planet. Geostationary orbits, on the other hand, keep satellites fixed above a specific location, making them perfect for monitoring weather or communications.
When a satellite flies over an area, its sensors start collecting data in the form of electromagnetic radiation. Different types of sensors capture different kinds of information. For instance, optical sensors gather visible and infrared light, while microwave sensors are special because they can go through clouds and collect data even during storms or at night.
Once the satellite has collected all its data, it sends it back to Earth using radio waves. The information is received by special ground stations located all over the world. These stations make sure that the satellite can stay in contact with Earth, sending the data back quickly for analysis.
After the data is received, it needs to be processed so that it can be turned into useful satellite imagery. This processing includes things like correcting errors caused by the atmosphere, calibrating the images, and making sure the images match up with the correct locations on Earth. This is called georeferencing, and it ensures that the images we see are accurate representations of the real world.

Satellite imagery is a powerful tool that helps us see and understand the Earth from above. It provides data that would be impossible to get from the ground. For example, satellite imagery allows us to track deforestation, monitor ocean temperatures, or even see how new developments affect land. This bird’s-eye view gives us the ability to make smarter decisions about how we treat our planet.
Satellite imagery is important in many industries, such as agriculture, urban planning, and disaster management. It helps farmers monitor crop health, gives city planners valuable insights to build better infrastructure, and helps with the early detection of disasters. With satellite imagery, we can capture clear and detailed images of the Earth’s surface, making it easier for decision-makers to understand what’s happening on the ground.
Overall, satellite imagery has transformed how we view and manage the world around us. It’s an essential tool that helps manage resources, track weather patterns, and even build new cities. With the right satellite imagery, industries can innovate, plan, and react in real time, driving growth and improving efficiency. By working with companies like XRTech Group, you gain access to accurate, up-to-date satellite imagery that will help make your projects more successful, whether it’s monitoring the environment, responding to disasters, or planning for future growth.
Satellite imagery refers to the process of capturing pictures or data of the Earth’s surface from satellites orbiting high above us. These images are used in many industries, from agriculture to urban planning and even space research. There are different types of satellite imagery, each designed for specific purposes. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types and how they work:
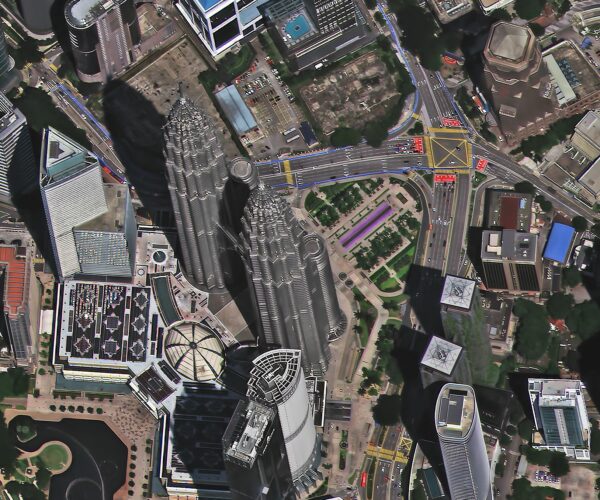

Optical imagery is one of the most commonly used forms of satellite imagery. It works just like a regular camera but from space. These satellites capture images in the visible spectrum, which means they can “see” what human eyes see.
Visible Light: This type of imagery captures photos in the same way you would take a picture with your phone. It’s great for general visual purposes like observing cities, forests, or oceans.
Multispectral: This is an upgrade to visible light images, as it captures data at different wavelengths, including visible light and near-infrared. This allows for more detailed views, like detecting plant health or water quality.
Hyperspectral: Imagine multispectral but with even more layers. This type captures a wide range of wavelengths, providing a detailed analysis of the Earth’s surface. It’s used for in-depth studies like finding minerals or monitoring environmental changes.
Who uses it? Environmental scientists, urban planners, and agriculture experts use multispectral and hyperspectral imagery to monitor land use and vegetation health. It’s also useful for tracking environmental changes over time.
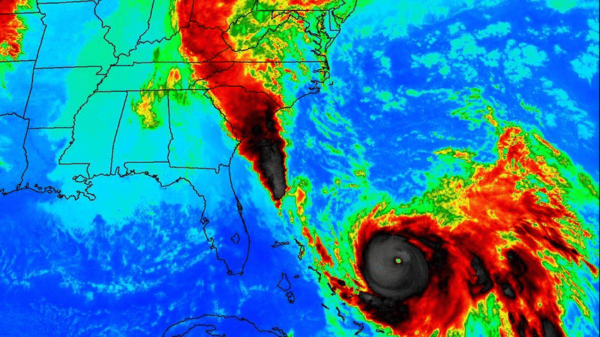
Infrared imagery is super helpful for seeing things that are not visible to the naked eye, like heat or water. This type of satellite imagery is essential for monitoring vegetation, water bodies, and even detecting heat sources.
Near-Infrared (NIR): It helps spot vegetation health and water bodies. Plants reflect near-infrared light differently than other surfaces, making it easier to track their condition.
Shortwave Infrared (SWIR): This type helps find minerals and analyze soil. It’s particularly useful for geologists and environmental researchers.
Thermal Infrared (TIR): Measures heat radiation, which can be used for detecting wildfires, monitoring energy usage, or tracking temperature changes in oceans or land.
Who uses it? Infrared imagery is widely used in agriculture to monitor crops and water bodies. Environmental agencies also use it for forest health monitoring and disaster management, like spotting wildfires early on.
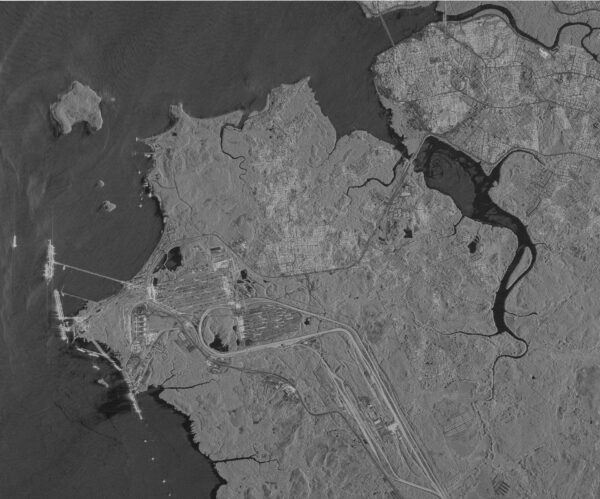

Radar imagery is a unique type of satellite imagery that uses microwave signals instead of visible light. This means it can capture high-resolution images even in cloudy weather or at night. This is especially useful in regions that experience constant cloud cover or during nighttime operations.
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR): A key feature of SAR is that it can work in any weather conditions, even when there’s a lot of cloud cover. It is used to study large areas, like forests or oceans, and can detect changes on the ground over time.
Interferometric SAR (InSAR): InSAR is used to measure ground movement, like monitoring earthquakes, volcanoes, or even small shifts in the ground due to construction. It’s excellent for tracking changes in the Earth’s surface.
Who uses it? SAR and InSAR are valuable for industries like disaster management, mining, and construction. Governments and military organizations use it for monitoring infrastructure and tracking environmental changes.

Panchromatic imagery captures high-resolution black-and-white images. These images are sharp and offer excellent spatial details. They are perfect for creating detailed maps or measuring distances between objects.
Who uses it? Panchromatic imagery is often used for mapping and creating detailed geospatial data, especially in urban planning and city infrastructure projects. It’s also used by surveyors and land planners for accurate measurements.
Lidar imagery uses laser pulses to measure distances and create 3D representations of the Earth’s surface. This technology allows us to build highly accurate and detailed maps, even in areas with heavy vegetation. It’s used for creating precise topographical maps or measuring land elevation changes.
Who uses it? Lidar imagery is commonly used in forestry, mining, and environmental management. It helps in creating 3D maps of forests, studying soil erosion, and managing natural resources.
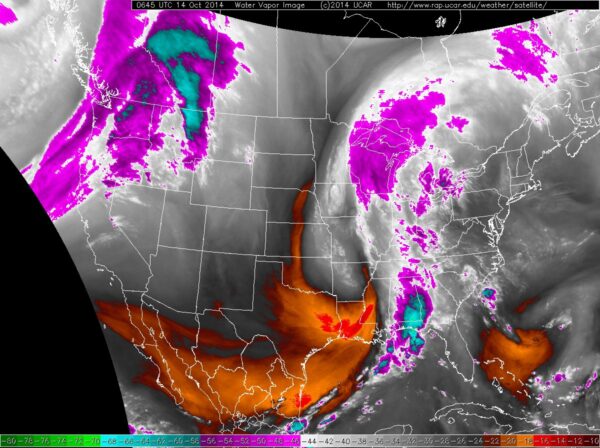
Water vapor imagery refers to a type of satellite imagery that focuses on detecting and analyzing the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere. This imagery is captured using specialized sensors on satellites that can detect moisture levels in the air, even in areas where there is no visible cloud cover. It plays a key role in weather forecasting and understanding atmospheric conditions.
Water vapor imagery works by using infrared sensors that detect the temperature of water vapor in the atmosphere. Water vapor, being a greenhouse gas, absorbs and emits infrared radiation differently than other gases in the atmosphere. By measuring this radiation, satellites can create images that show the distribution and movement of water vapor across the Earth.
Meteorologists and weather agencies use water vapor imagery extensively to enhance their weather forecasts and understand storm development. It is also valuable to climate researchers, helping them understand trends in atmospheric moisture and its impact on global weather patterns.
Geostationary imagery comes from satellites that remain fixed above a particular point on Earth. These satellites continuously monitor the same area, providing real-time updates and making them essential for weather forecasting.
Who uses it? Geostationary imagery is essential for meteorologists, disaster management teams, and even climate scientists to track weather patterns and climate change.
Each type of satellite imagery serves a unique purpose, helping different industries make better decisions. Whether it’s optical imagery for urban planning, infrared imagery for crop health, or radar imagery for disaster response, these images provide the crucial data needed to monitor and manage the Earth’s surface. With satellite imagery, you can explore new possibilities, track changes, and make informed decisions that shape the future.
Satellite imagery is transforming industries with its ability to capture detailed visual data of Earth’s surface. Its applications are diverse and continue to evolve, offering a wide range of benefits to various sectors. Let’s explore how satellite images are used across different fields:
One of the most impactful uses of satellite imagery is monitoring changes over time. By analyzing high-resolution images, experts can:
With this information, governments, NGOs, and urban planners can make informed decisions to manage resources better and mitigate negative impacts.
Environmental conservation heavily relies on satellite imagery to keep an eye on the planet’s health. Here’s how:
Through sophisticated sensors on satellites, this data helps in creating land cover maps, tracking biodiversity, and even assessing areas prone to ecological risks. These insights are vital for policies aimed at preserving nature.
The role of satellite imagery in weather forecasting is indispensable. It allows meteorologists to:
This real-time data improves the accuracy of weather predictions, which benefits everything from daily forecasts to disaster preparedness plans.
Managing infrastructure is critical for urban development and disaster prevention. Satellite imagery supports:
For decades, satellite imagery has been a critical tool for military and defense operations. High-resolution satellite photos provide essential data for:
By integrating GIS and satellite technology, the military gains enhanced situational awareness, improving mission success and decision-making. This fusion ensures that troops are better prepared for challenges in dynamic environments, whether on the battlefield or during humanitarian missions.
Building sustainable cities and infrastructure requires precise data, and satellite imagery plays a vital role. Here’s how:
This combination of data ensures smarter urban growth, efficient resource use, and a balance between development and environmental preservation.
When natural disasters strike, satellite imagery becomes indispensable for saving lives and mitigating damage. It provides:
By using this data, GIS experts create hazard maps and assist authorities in preparing for future disasters. This proactive approach enhances community resilience and minimizes the impact of emergencies.
Governments worldwide rely on satellite imagery for a range of critical functions, such as:
This data enables better governance, resource allocation, and policy-making to serve citizens effectively.
Satellite imagery plays a crucial role in creating detailed maps of Earth’s surface. These maps provide essential insights and are used across industries for purposes like:
With advancements in satellite technology, maps now offer unprecedented accuracy, empowering organizations to make informed decisions in real time.
The agricultural sector benefits immensely from satellite imagery, as it helps improve productivity and sustainability. Here’s how:
These applications make agriculture more efficient and sustainable, supporting food security across the globe.
Water is one of the most precious resources, and satellite imagery is a powerful tool for its conservation. This includes:
By leveraging satellite data, policymakers and environmentalists can work toward better water conservation strategies.
Maritime security is another critical area where satellite imagery proves invaluable. Applications include:
This real-time monitoring enhances safety and security for global maritime operations.
The oil and gas industry also depends heavily on satellite imagery to optimize operations. Key applications include:
By utilizing the latest advancements in satellite imagery, the oil and gas sector can improve efficiency while reducing its environmental footprint.
Satellite imagery is revolutionizing construction planning and monitoring by providing precise data for site evaluation and development.
This data-driven approach reduces costs and enhances efficiency, making construction projects safer and more sustainable.
Mining operations benefit greatly from the use of satellite imagery for exploration and environmental management.
With satellite data, mining becomes more sustainable and efficient, reducing unnecessary exploration costs.
The electrical and power sector relies on satellite imagery to maintain infrastructure and improve energy distribution.
This technology supports smarter energy grids and helps transition to cleaner energy sources.
Fighting pollution is easier with the help of satellite imagery, which provides real-time data for environmental assessments.
These insights empower governments and organizations to implement effective pollution control strategies, fostering healthier ecosystems.
National security is one of the most critical applications of satellite imagery.
With advanced radar and optical imaging capabilities, satellite data ensures countries can protect their citizens and critical infrastructure.
Humans can only see a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum—the visible light we encounter daily. However, satellite sensors go beyond this limitation, capturing light types such as infrared light, ultraviolet light, and even microwaves. To make this invisible data useful, satellites assign visible colors to these light forms, resulting in images with “unnatural” but meaningful colors.
These advanced capabilities allow satellites to uncover details that are invisible to the human eye. For instance, smooth surfaces like roads reflect energy in one direction (specular reflection), while rough surfaces like forests scatter energy in multiple directions (diffuse reflection). This information helps scientists monitor forest density and track changes in vegetation over time, offering insights into the Earth’s natural processes.
Different objects on Earth react uniquely to various wavelengths of radiation. For example, a specific frequency of infrared light can reveal plant health. Healthy leaves reflect this frequency effectively, while unhealthy ones absorb more of it. By analyzing these differences, experts can assess vegetation health, track agricultural productivity, and even detect environmental changes.
This ability to measure and interpret radiation makes satellite imagery an essential tool for industries like agriculture, forestry, and environmental management. It turns complex data into actionable insights, allowing us to better understand and care for our planet.
Satellites gather valuable information by detecting how energy interacts with the Earth’s surface. Using remote sensing sensors, they measure electromagnetic radiation in three forms: reflection, emission, and a mix of both. These measurements provide detailed insights into land, vegetation, water, and even urban areas.
Light, as a wave, is characterized by its wavelength and frequency. Longer wavelengths carry less energy, while shorter ones are more powerful. This dynamic is key to how satellites interpret data across the electromagnetic spectrum.
The electromagnetic spectrum is vast, but not all wavelengths are equally useful for observing the Earth’s surface. In remote sensing, specific ranges are employed to highlight unique features:
Visible Light:
Near-Infrared (NIR):
Mid-Infrared (SWIR):
Satellites are equipped with two critical types of resolution:
Another important factor is revisit time, the interval at which a satellite observes the same location on Earth. Revisit times depend on factors like orbit, altitude, and coverage area. These intervals are vital for tracking changes, performing time-series analysis, and ensuring timely monitoring of critical events.
Through this precise and systematic approach, satellite imagery continues to provide actionable data, empowering industries to make informed decisions for a better future.
Satellite imaging is rapidly evolving, with new technologies and advancements making it an even more powerful tool for understanding our planet. As we look to the future, here are some key trends that will shape the satellite imaging industry:
As technology improves, satellites are capable of capturing even higher resolution imagery. This means we will soon be able to see more details from space, with pixels becoming smaller and more precise. This trend is expected to revolutionize industries like urban planning, agriculture, and environmental monitoring by providing clearer, more accurate data.
The future of satellite imaging will also include more frequent data collection. With the rise of small satellite constellations, satellites will be able to revisit areas more often. This increased revisit frequency will allow for real-time or near-real-time monitoring, helping industries make faster decisions and respond to changes more quickly.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are expected to play a significant role in satellite imaging. These technologies can process vast amounts of data, detect patterns, and even predict future trends. AI can automate the analysis of satellite images, making it easier to identify critical changes on the ground, such as deforestation, urbanization, or natural disasters.
Advances in multi-spectral and hyper-spectral imaging will allow satellites to capture a wider range of wavelengths. This will improve the ability to monitor a variety of surfaces, from vegetation health to water quality and pollution levels. Hyper-spectral imagery, in particular, can help detect specific materials and substances on the Earth’s surface, providing even more valuable insights.
Smaller and more affordable satellites are becoming increasingly popular. These small satellites (or CubeSats) can be launched in large numbers, forming constellations that provide more frequent and detailed coverage. As the cost of building and launching satellites decreases, satellite imaging will become accessible to even more industries and organizations.
Satellite imagery will be integrated with other types of data, such as IoT (Internet of Things) sensors, ground-based observations, and weather data. This integration will provide a more comprehensive picture of what’s happening on the Earth’s surface, improving decision-making and enabling more accurate forecasting.
In the future, accessing and analyzing satellite imagery will become easier. With user-friendly platforms and software, more people and organizations will be able to access high-quality imagery, even without a technical background. This democratization of satellite data will allow industries like agriculture, urban development, and disaster management to use satellite imagery in their everyday operations.
The satellite imagery market is experiencing significant growth, with projections indicating it will exceed $8 billion by 2033. This expansion is driven by advancements in high-resolution and 3D imaging technologies, enhancing the quality of Earth monitoring. The increased demand for satellite imagery in sectors like agriculture, environmental monitoring, and defense is contributing to this market growth.
If you’re looking to harness the power of satellite imagery for your business or government needs, XRTech Group is the perfect partner to help you get started. With over 60 satellites supporting industries across the globe, we offer a comprehensive suite of satellite imagery services that can be tailored to your specific needs.
Here’s why you should choose XRTech Group for satellite imagery:
Wide Range of Satellites
XRTech Group operates a diverse fleet of over 60 satellites, including optical, SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar), and high-resolution systems. This wide range allows us to provide precise imagery, no matter the weather conditions or lighting. Whether you need imagery for urban planning, environmental monitoring, or defense, we have the right tools to meet your requirements.
Global Reach
Our satellite fleet serves clients across various sectors worldwide. We help government agencies, businesses, and industries get accurate data that supports informed decision-making. Whether you’re working in agriculture, energy, defense, or construction, XRTech Group provides valuable insights for your needs on a global scale.
Value-Added Services
At XRTech Group, we don’t just stop at delivering imagery. We offer additional value-added services that enhance the utility of satellite imagery for your projects:
Comprehensive Solutions
From optical imagery to SAR, 3D models, and change detection, XRTech Group provides a full spectrum of satellite imagery services. We support various industries, including agriculture, mining, environmental monitoring, construction, and defense, by turning complex satellite data into actionable insights.
Expert Support
Our team of experts will guide you every step of the way. Whether you’re new to satellite imagery or an experienced user, XRTech Group provides dedicated support to ensure you’re maximizing the value of the data you receive.
Customizable Plans
We understand that every business has unique needs. That’s why we offer customizable packages for satellite imagery services, tailored to your budget and project requirements. From simple image access to advanced analysis, we are here to help you.
If you’re ready to take advantage of satellite imagery and all the insights it offers, reach out to XRTech Group. Our team is ready to provide you with the tools and support you need to make data-driven decisions, no matter your sector. Whether it’s for urban planning, environmental analysis, or defense applications, XRTech Group is here to help you unlock the power of satellite imagery.
Satellite imagery has become a vital tool for businesses and governments worldwide, enabling precise data collection and informed decision-making across various sectors. Here are some notable examples:
Tracking Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Companies are increasingly utilizing satellite imagery to monitor and reduce emissions within their operations and supply chains. The tracking of greenhouse gases, particularly methane, has become a focus due to its significant impact on global warming. Organizations like Terrabotics, GHGSat, and Momentick are leading efforts to utilize space-based technologies for emission tracking, leveraging data from small satellites and large constellations like the EU’s Copernicus. While satellite imagery can be expensive, the broader view it offers is invaluable for emissions monitoring. Regulations in the EU and US are pushing industries to adopt these methods. Although the use of satellites for tracking CO₂ emissions is developing, challenges remain due to high baseline atmospheric CO₂ levels. Other pollutant emissions are also being targeted for future space-based monitoring improvements. The integration of space-based data into industries is growing, with the potential to significantly reduce emissions and enhance operational efficiency, particularly in sectors such as aviation and shipping. However, the industry must demonstrate the cost-effectiveness and seamless integration of such data into business practices. ~ Financial Times
Disaster Response and Recovery: During natural disasters, satellite imagery provides real-time data to assess damage, plan relief efforts, and monitor recovery progress. For instance, after hurricanes or earthquakes, governments and aid organizations use satellite imagery to identify affected areas, estimate damage, and coordinate response strategies effectively.
City-Scale Decision-Making: During the COVID-19 pandemic, satellite imagery was employed to monitor human and economic activities, aiding city-scale decision-making. By analyzing changes in urban areas, authorities could assess the impact of lockdowns and plan recovery strategies. This approach demonstrated the potential of satellite imagery in providing insights into economic indicators and social behaviors during unprecedented times. ~Arxiv
Infrastructure Monitoring: Governments utilize satellite imagery to monitor infrastructure development, ensuring compliance with regulations and assessing the impact of new projects on the environment and surrounding communities. This practice helps in making informed decisions regarding urban expansion and resource allocation.
Retail and Economic Activity Analysis: Companies like Orbital Insight analyze satellite imagery to estimate retail revenue by studying car counts at malls, helping insurance companies assess damage from natural disasters, and monitoring oil storage facilities to gauge a country’s fuel supply. This data assists businesses in making strategic decisions based on real-time economic activities. ~ Wikipedia
Supply Chain Management: Businesses use satellite imagery to monitor supply chain activities, such as tracking the movement of goods and assessing the health of agricultural products. This information helps in optimizing logistics and ensuring the quality of products delivered to consumers.
Deforestation Monitoring: Environmental organizations employ satellite imagery to monitor deforestation rates, enabling them to track illegal logging activities and assess the effectiveness of conservation efforts. This data is crucial for developing strategies to protect forests and biodiversity.
Agricultural Planning: Farmers and agricultural businesses use satellite imagery to assess crop health, monitor soil moisture levels, and predict yields. This information aids in making informed decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and harvesting, leading to improved productivity and sustainability.
These examples illustrate how satellite imagery serves as a powerful tool for accurate data collection and decision-making across various sectors globally. Its ability to provide real-time, comprehensive insights makes it indispensable for businesses and governments aiming to enhance efficiency, sustainability, and resilience.
Satellite imagery refers to the process of capturing visual data of the Earth’s surface using satellites that orbit the planet. These satellites capture images in different wavelengths, including visible light, infrared, and microwave, to provide detailed information about the environment.
Businesses use satellite imagery for various purposes such as monitoring land use, tracking environmental changes, managing resources, and enhancing supply chain operations. It helps businesses make informed decisions based on real-time, accurate data.
There are several types of satellite imagery:
Various industries benefit from satellite imagery, including agriculture, construction, defense, environmental monitoring, and urban planning. Governments, businesses, and environmental agencies use it for tasks like disaster management, resource management, and environmental conservation.
The accuracy of satellite imagery depends on the satellite’s resolution. High-resolution satellites can provide incredibly detailed images, down to a few centimeters. Lower-resolution satellites might show broader views but are still useful for larger-scale analyses.
Satellites capture images on a regular basis, with some having revisit times of 1 to 3 days. This means they can observe the same area frequently, which is ideal for monitoring changes, such as deforestation, crop health, or urban growth.
Yes, satellite imagery plays a crucial role in monitoring climate change. It helps track changes in land use, deforestation, ice cap melting, and greenhouse gas emissions, providing valuable data for scientists and policymakers working to mitigate climate change.
XRTech Group provides access to high-quality satellite imagery through its services, with the option of acquiring data from over 60 satellites. Customers can get tailored imagery for specific needs, such as Digital Elevation Models (DEM), Digital Orthophoto Maps (DOM), and more.
Satellite imagery in agriculture helps farmers monitor crop health, soil moisture, and pest outbreaks. It allows for precision farming, optimizing irrigation, fertilization, and harvesting, leading to increased productivity and sustainability.
XRTech Group offers over 60 satellites that provide high-resolution and accurate satellite imagery for businesses and governments worldwide. We specialize in value-added services like DEM, DOM, City Models, SAR, and Optical imagery, helping you make data-driven decisions in any sector.

Tailings Dam Monitoring: How Advanced Satellite Intelligence Is Transforming Tailings Dam Safety Tailings dams are among the most critical—and high-risk—structures
From Visible Light to Spectral Intelligence in Modern Satellite Remote Sensing Satellite imaging has moved beyond photography. For decades, Earth

For a limited time, get high-resolution 30cm new tasking satellite images Free.
✅ Crystal-clear 30cm resolution
✅ Fast & accurate satellite data collection
✅ Exclusive offer for registered users only