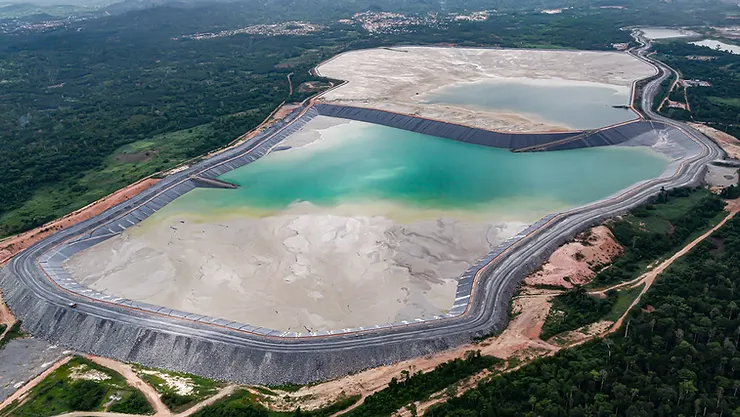

Tailings Dam Monitoring with InSAR & AI
Tailings Dam Monitoring: How Advanced Satellite Intelligence Is Transforming Tailings Dam Safety Tailings dams are among the most critical—and high-risk—structures

Who invented the drone, and when was the first drone invented? These are questions that lead us to the fascinating journey of drones, or unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). A drone is a flying machine that can be remotely controlled or programmed to fly on its own. It comes in different sizes, shapes, and designs. Drones are used for many purposes, like taking pictures, delivering packages, searching for missing people, watching over areas, and even in military missions.
The history of who invented drones goes back over two centuries. While today’s drones are packed with advanced features, the earliest UAVs were simple machines. The first recorded use of UAVs happened in the 20th century. Abraham Karem, often called the “father of UAV technology,” played a significant role in advancing drones to what we know now.
Drones are now an essential part of our daily lives, from military operations to helping farmers monitor crops. Let’s take a closer look at how this amazing invention started and grew over time.
The question of “Who invented the drone” leads us to Abraham Karem, who is often called the “Father of UAV Technology.” He invented the first major drone in the 1970s. Karem, an engineer with a passion for aviation, was born in Baghdad and grew up in Israel before moving to the United States in the 1970s. His innovative work laid the foundation for modern drones.
In the U.S., Karem founded companies like Leading Systems, Inc., and Karem Aircraft. His early creation, a drone prototype called the Albatross, marked the beginning of significant advancements in unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). This prototype was heavy, weighing around 200 pounds, but it caught the attention of DARPA (Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency) and the U.S. military.
Under DARPA’s guidance, Karem refined the Albatross into what became the Predator drone. The Predator, developed in the 1990s, became a groundbreaking UAV used for surveillance and combat missions. Its success in reconnaissance and military operations demonstrated the vast potential of drones.
Karem’s inventions not only shaped military applications but also opened the door for civilian drones, influencing their design and functionality. His pioneering work in autopilot systems for UAVs made drones more efficient and reliable, playing a crucial role in advancing drone technology.
Today, when asking “When was the first drone invented?”, the 1970s stand out as a pivotal time in history. Abraham Karem’s innovations continue to inspire modern drone designs, making him a key figure in UAV development.
Karem’s efforts have been recognized with awards like the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum Trophy for Current Achievement in 1998. His legacy lives on, influencing both military and civilian UAV advancements worldwide.
The invention of drones wasn’t the work of just one person. It was a journey of many discoveries and improvements over time. Who invented the drone is a question tied to the progress of technology through history. The idea of flying without a pilot began as early as the 19th century. Back in 1783, the Montgolfier brothers from France launched the first unmanned hot air balloon. While it wasn’t a modern drone, it marked the start of exploring unmanned flight.
By 1898, Nikola Tesla created the first radio-controlled aircraft. This groundbreaking invention allowed machines to be controlled from a distance without a pilot onboard. This concept of remote control became an essential part of who invented drones and how they work today.
In the early 20th century, drones began to take shape for military uses. As technology improved, these unmanned aircraft became more advanced and were designed to handle a variety of tasks.
The drones we see today became possible due to several major advancements:
Thanks to these improvements, drones are now used for many purposes. From aerial photography and delivery to rescue missions and military operations, they’ve become essential tools. When we ask, “When was the first drone invented?”, we are looking at a timeline of discoveries and innovations that span centuries.
This history shows how technology has evolved, paving the way for modern drones. XRTech Group continues to lead by offering advanced drones designed for today’s needs.
The story of drones is long and exciting, filled with amazing achievements and breakthroughs. Below is a timeline showing the journey of drones, from simple beginnings like unmanned balloons to the advanced drones we use today.
The first unmanned hot air balloon was launched by Joseph-Michel and Jacques-Étienne Montgolfier in France. Made from linen and silk, this balloon used a stove burning wool and straw for fuel. It rose about 6,000 feet and traveled over a mile in just 10 minutes. This was the first recorded use of unmanned aircraft and an important step toward who invented drones.
In 1849, the Austrian army used unmanned balloons filled with explosives to attack Venice. However, the attempt was not very successful because the wind caused many of the balloons to miss their targets. This marks one of the earliest answers to when was the first drone invented for military purposes.
Nikola Tesla created the first radio-controlled boat in 1898. Although this invention was used on water, it showed the potential for remotely controlled vehicles, inspiring later ideas of unmanned aerial systems. This was a key moment for those wondering who invented the drone and how remote control technology began.
Charles F. Kettering built the first unmanned aerial torpedo, called the Kettering Aerial Torpedo or “Bug.” This device could fly at about 50 mph and cover up to 75 miles. Even though it wasn’t used in combat, it helped shape early drone technology and answers the question of when was the first drone invented.
The British Royal Navy created the de Havilland DH82B “Queen Bee,” which was used as a target for training. This remotely controlled aircraft is often seen as the first modern drone. The word “drone” is believed to have come from its buzzing sound, much like a bee. This marks a turning point in understanding who invented drones.
The US started its drone program with the Curtiss N2C-2, also called the Radioplane. These drones were used during World War II to train gunners. Over 60,000 models were eventually produced, solidifying America’s early steps in unmanned aviation.
The U.S. Air Force and Boeing experimented with the BQ-7, which allowed pilots to remotely guide planes loaded with explosives. This was one of the first uses of first-person view (FPV) technology. Though not very effective in war, it paved the way for modern FPV drones.
During the Vietnam War, the US used over 3,400 Ryan Model 147 drones. These unmanned aircraft performed multiple tasks, like surveillance and acting as decoys. This era advanced drone capabilities and highlighted who invented drones for broader military uses.
The US Navy introduced the RQ2 Pioneer during the Gulf War for surveillance and reconnaissance. It became one of the first widely used modern drones.
Abraham Karem’s work led to the MQ-1 Predator drone. Released in 1996, it became a game-changer in military surveillance and targeted missions. The Predator is now iconic in discussions of who invented the drone and its evolution.
In 2006, drones were allowed in US civilian airspace under certain rules. This opened the door for drones to be used in industries like agriculture, photography, and deliveries. It also brought drones closer to everyday life, addressing when was the first drone invented for non-military uses.
DJI launched the Phantom drone, making drones easy to use and affordable for consumers. This breakthrough sparked massive interest in personal and commercial drone use. It also cemented DJI as a leader in the field for anyone exploring who invented drones for modern applications.
The journey of drones has been incredible. Starting as simple unmanned balloons in the 18th century, drones have become powerful tools for many industries today. Early experiments like Tesla’s radio-controlled boat and Kettering’s aerial torpedo showed the potential for unmanned vehicles. Over time, drones transformed from military tools into devices used for filming, delivery, and even farming.
As drones continue to evolve, they shape industries and everyday life. The history of who invented the drone shows how far we’ve come and gives us a glimpse of where this amazing technology might go next.
Drones come in many shapes and sizes. Each type is designed for a specific use. Below are some of the most common types of drones.
Military drones are some of the most advanced drones ever created. They are used for spying, keeping watch, and even for combat. Famous examples include the Predator drone and the RQ-4 Global Hawk. These drones are built for high-tech missions and play a key role in defense.
Consumer drones are made for fun activities and hobbies. Many people use them for taking pictures or videos. Popular examples include the DJI Phantom and Mavic series. These drones are easy to use and are perfect for photography and filming.
Commercial drones are built for work. They are often used in industries like farming, construction, and energy. These drones have special cameras and sensors to handle tasks such as inspecting buildings or mapping land.
A special kind of commercial drone, agricultural drones help farmers. They are designed to monitor crops, analyze soil, and assist with watering. These drones save farmers time and effort.
Delivery drones are made to transport packages. Companies like Amazon and Google are working on creating drones that can deliver items to your doorstep. These drones are designed to move through busy areas like neighborhoods or cities.
Racing drones are made for speed and competition. These small drones are equipped with cameras so pilots can see from the drone’s perspective. They are controlled with precision and used in fast-paced drone racing events.
Some drones combine features from different types. For example, a consumer drone might include tools for business use. These hybrid drones offer flexibility for both fun and work.
Thermal camera drones have special cameras that detect heat. They are used for jobs like finding people during search-and-rescue missions or checking for heat problems in machines. These drones are a perfect mix of technology and safety.
Underwater drones are built to explore beneath the surface. These drones are used for ocean research, underwater inspections, or even filming in water.
AI drones are advanced drones powered by artificial intelligence. They can make decisions without constant human control. These drones are used for tasks like tracking objects, avoiding obstacles, and even performing complex missions. With AI, drones can analyze data in real time, making them ideal for industries like delivery, surveillance, and disaster response. They combine smart technology with precision, helping to make work faster and more accurate.
Each type of drone serves a unique purpose. Whether for fun, work, or special missions, there is a drone for every need.
Anti-drone technology includes tools and methods used to spot, follow, and stop drones that could harm public safety, national security, or privacy. Let’s explore the most common ways these systems work:
While anti-drone technology can protect people and places, it has raised concerns about privacy and civil rights. Legal and safety rules often limit how and where this technology can be used.
This technology ensures security but must be handled carefully to respect everyone’s rights.
Drones, also called unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), have many great uses, but they also come with some challenges. Let’s take a look at the main drawbacks of drones:
Drones with cameras and other sensors can easily invade people’s privacy. When we ask “who invented the drone,” we also need to think about how drones can sometimes cause problems with privacy. People are concerned about drones flying into private spaces and taking photos or videos without permission.
Drones can be a safety risk, especially when flying near other aircraft or crowded areas. Drones can sometimes interfere with commercial flights or emergency services. If you wonder “who invented drones,” remember that these early ideas have led to drones becoming a possible hazard when not used carefully.
Drones could be used for harmful purposes, such as spying on others or even delivering dangerous items like weapons. This poses a serious threat to security, especially for important places like government buildings or military sites. It’s important to consider “when was the first drone invented” to understand how drones evolved from helpful devices to potential security risks.
Some drones can make loud noises that disturb people living in neighborhoods or even wildlife. Noise from drones can be annoying and may cause problems, especially in areas where peace and quiet are important.
Governments around the world have created rules to control the use of drones. These rules can be different in each country. Some places may not allow drones in certain areas, like near airports or in certain cities, which can limit how drones are used.
Drones can be expensive. For some people or small businesses, the price of a drone is too high. This means not everyone can afford to use them, even though drones could be useful in many situations.
The future of drone technology is bright, with many exciting changes coming soon. Drones will continue to evolve, and here’s what we can expect:
Autonomous Drones: Drones will likely become more independent. Who invented the drone started with basic controls, but soon they will be able to fly complex missions without much human help.
AI and Machine Learning: As AI and machine learning improve, drones will be able to make real-time decisions. They will learn from their environment and adapt. This means drones can fly in changing conditions and perform tasks more efficiently.
Improved Flight Performance: Drones will become faster, lighter, and have a longer range. This is due to advancements in the materials used to build them and better aerodynamics. These improvements will allow drones to carry more weight and go farther.
5G Integration: With the growth of 5G networks, drones will be able to communicate faster and more reliably with their operators. This will make it easier for large groups of drones to work together safely and efficiently.
Increased Use in Many Industries: Drones are already being used in many industries, but in the future, their use will grow even more. Drones will be used in farming, construction, delivery, and more, helping improve efficiency and safety in these areas.
Regulation and Safety: As drones become more common, it will be important to have rules in place to keep them safe. Governments will likely create more regulations to make sure drones are used responsibly.
The future of drone technology looks promising, with many new possibilities. Who invented drones started it all, and now the technology is changing industries and improving lives. However, privacy and security will also need to be managed carefully as drones become more common.
In the years ahead, drones will be able to do even more amazing things. One exciting idea is urban air mobility, where drones could transport people in cities, helping reduce traffic. Companies like Uber and Airbus are working on this.
Drones will also play a larger role in national security, with better technology for stealth and longer flight times.
On the consumer side, drones will become easier to use, with better cameras and longer battery life. 5G will help improve the communication between drones and operators, making it easier to control them.
In the military, drones will be used more for security and defense, and even in swarm technology, where many drones work together on big tasks.
As drones become more popular, there will be more rules to follow. Governments will create safety guidelines to ensure drones are used safely, and privacy concerns are addressed.
Drones have become popular tools in many industries. They are used for many different tasks. Let’s take a look at the top 10 applications of drones.
Delivery Services Drones are now used for delivery. They can deliver packages quickly. This makes it easier for companies to get products to customers faster. Many people are asking, “Who invented the drone that could do this?” The first drone with delivery capabilities was created in the 21st century.
Agriculture In farming, drones are used to monitor crops. They help farmers see how their crops are growing. This makes it easier to spot problems early and take care of them. So, when was the first drone invented for agriculture? It was developed in the early 2000s to help farmers.
Search and Rescue Drones are also used to find missing people. They can reach places that are hard to get to. This is why they are helpful in search and rescue operations. Many people wonder, “Who invented drones that can help save lives?” The use of drones for rescue was first explored in the early 2000s.
Construction In construction, drones are used to take pictures and videos of buildings. They help check how work is going on a site. This helps builders keep track of progress. So, who invented drones for construction monitoring? The first drone used in construction was introduced in the 2010s.
Surveillance Drones are used for surveillance. They can fly high and watch over large areas. This helps with security and keeping people safe. People often ask, “When was the first drone invented for surveillance?” It was developed in the early 2000s for military and police use.
Environmental Monitoring Drones help with environmental monitoring. They can check pollution levels, track wildlife, and study forests. When was the first drone invented for environmental use? It was created in the 2000s to help scientists.
Photography Photography is another big use for drones. They can take amazing photos from the sky. This helps photographers capture pictures of places from a new angle. Many wonder, “Who invented drones for photography?” The first drone for photography was made in the 2000s.
Mapping Drones are now used for mapping. They can create detailed maps of areas that are hard to reach. This is very useful for geographers and scientists. When was the first drone invented for mapping? It was introduced in the 2000s for land surveys.
Military Uses Drones are used by the military for surveillance and gathering information. They can help keep soldiers safe by watching enemy movements. So, who invented drones for military use? The first drone for military purposes was created in the 20th century.
Entertainment In entertainment, drones are used in movies and shows. They help filmmakers get shots that would be hard to take from the ground. Many people ask, “Who invented the drone for entertainment?” The use of drones in film started in the 2010s.
XRTech Group offers a wide range of drone products perfect for various tasks, which can be easily purchased directly from XRTech. Here is an overview of some of the top drone options:
Autel EVO 2 Dual 640T Enterprise V3: This drone is great for inspections and other detailed tasks. It has two cameras: a high-quality RGB camera and a thermal imaging camera. The thermal camera helps find heat leaks, and it works with ±3°C accuracy. It has intelligent flight modes, 38 minutes of flight time, and 360-degree obstacle avoidance.
DJI Mavic 3 Enterprise (especially the 3T model): The DJI Mavic 3T is perfect for professional tasks that need high-quality visuals. It combines high-quality visuals with great thermal imaging. The thermal camera has a 640 x 512 resolution, and it includes spot and surface temperature measurements. Its visual camera has 48 MP with a 56x hybrid zoom. It also includes obstacle avoidance for safety.
Autel EVO II Pro V3: This drone has a 20MP 1-inch CMOS sensor and can shoot in up to 6K resolution, making it great for various tasks. It also has 4K HDR video and SkyLink 2.0 video transmission, providing smooth, clear images. Plus, it features 360-degree obstacle avoidance.
DJI Mavic 3: This drone has a 4/3 CMOS Hasselblad camera, perfect for professional images. It offers up to 46 minutes of flight time and has omnidirectional obstacle sensing. With its 5.1K video recording and waypoint flight function, it’s excellent for automated inspections.
DJI Matrice 350 RTK: Ideal for large-scale surveys, this drone has 55 minutes of flight time and can carry up to three payloads. It supports both thermal and high-resolution RGB cameras. It also has integrated RTK technology for precise measurements.
DJI Matrice 350 RTK: This drone is great for various industrial uses. It can carry up to three payloads at once, making it versatile for many types of work.
DJI Dock 2: This drone-in-a-box solution is perfect for autonomous drone operations. The drone can take off, land, and recharge automatically, making it suitable for different applications.
Autel EVO Nest and Autel Dragonfish Nest: These drone-in-a-box systems support various drones for different missions, such as inspections, mapping, and security tasks.
Camera Quality: High-resolution cameras are necessary for detailed images. Thermal cameras help find heat leaks and insulation problems.
Flight Stability: Stable flight is important, especially in windy conditions. Drones with GPS stabilization and powerful motors can help maintain stability.
Automated Flight Paths: These paths save time and ensure consistent results every time.
Obstacle Avoidance: This is important for safe flight, especially when flying near obstacles.
Durability: Choose a drone designed for long-term use and able to withstand tough conditions.
Weather Resistance: A weather-resistant drone will allow you to continue work in less-than-ideal weather.
Battery Life: Look for a drone that can fly for at least 25 minutes, allowing you to cover a larger area without interruptions.
Gimbal: A 3-axis gimbal ensures stable and smooth images during flight.
Partnership with China Siwei: XRTech works with China Siwei to provide high-resolution satellite imagery and advanced drone technology.
Comprehensive Solutions: XRTech offers geospatial solutions that combine satellite imagery, AI, software, and ground equipment.
Tailored Solutions: XRTech customizes solutions to meet the unique needs of each client.
Autonomous Operation: XRTech’s drone-in-a-box systems can operate automatically.
Real-Time Data and Analysis: XRTech drones capture and analyze data in real-time, providing instant results.
Versatility: XRTech’s drones can perform various tasks, such as inspections, mapping, and security patrols.
Secure Data Management: XRTech offers both cloud-based and on-premise data management for secure data handling.
The history of drones shows how humans have always worked hard to improve technology. From simple balloons and early radio-controlled planes to the modern drones we see today, drones have come a long way. Looking ahead, it’s clear that drones will keep growing in importance. They will change how we live, work, and interact with the world. Whether used for military purposes, business tasks, or personal enjoyment, the potential of drones is huge. They will continue to have a strong impact on society and will play an even bigger role in the future.
Drones, also known as UAVs (unmanned aerial vehicles), are quickly changing and have the power to transform many different industries. They’ve already made a big difference in fields like the military, delivery services, photography, and research. But, like all new technology, drones come with challenges. Issues like privacy, safety, noise, and high costs need to be carefully thought about. It’s important for governments, businesses, and people to think about these concerns while also enjoying the benefits drones offer.
As technology keeps improving, drones will only get better, offering new ways to do things and creating exciting new possibilities. If drones are used responsibly and with the right rules in place, they can help improve society and change the way we live and work.
The concept of drones has evolved over time, but one of the key inventors is Abraham Karem, who is often referred to as the “father of the drone.” He developed the first modern drone in the 1980s, known as the MQ-1 Predator. It was designed for military surveillance.
The first drone was invented in the 1930s, originally for military training purposes. However, modern drones, as we know them today, began to take shape in the 1980s, thanks to advancements made by engineers like Abraham Karem.
Drones for commercial use became more popular with companies like DJI, founded by Frank Wang in 2006. DJI revolutionized the commercial drone industry by making drones accessible for photography, surveying, and other applications.
The first drones were primarily used for military purposes. The earliest drones were created as target practice for anti-aircraft gunners and later evolved for surveillance and reconnaissance missions.
The title “father of drones” is often given to Abraham Karem, a pioneer in drone technology, especially for his development of the MQ-1 Predator, which became a crucial part of military operations.
Drones evolved from simple radio-controlled aircraft used for military training to sophisticated UAVs (unmanned aerial vehicles) with advanced cameras, GPS, and sensors. Over time, they were adapted for civilian and commercial purposes like aerial photography, surveying, and delivery.
Drones were initially designed for military purposes, but over the years, their use expanded to civilian and commercial sectors. Today, drones are used in industries like agriculture, film production, and even for personal recreation.
The first civilian drones were developed by companies like DJI. Frank Wang, the founder of DJI, played a key role in making drones more accessible to the public for personal use, such as flying for fun or for business applications like photography.
Technology played a major role in the invention of drones. Advancements in radio control, GPS navigation, camera technology, and battery life allowed drones to evolve from simple models to complex systems capable of flying autonomously with real-time data capture.
The first drones for commercial photography were made possible by the development of advanced UAV technology by companies like DJI. Their Phantom Series allowed drone pilots to capture high-quality aerial footage, revolutionizing industries like film production, real estate, and surveying.

Tailings Dam Monitoring: How Advanced Satellite Intelligence Is Transforming Tailings Dam Safety Tailings dams are among the most critical—and high-risk—structures
From Visible Light to Spectral Intelligence in Modern Satellite Remote Sensing Satellite imaging has moved beyond photography. For decades, Earth